Have you ever wondered why some people are willing to pay a lot for a product while others are only willing to pay a little? It all comes down to something called price elasticity. Price elasticity is a concept in economics that helps us understand how people react to changes in price. It’s like a superpower that businesses can use to make smart decisions about pricing.
In this article, I’m going to explain price elasticity and explain it in simple terms. I will also explain how to calculate it and what it means for businesses. Understanding price elasticity is crucial for setting the right prices and running a successful business.
So, if you’ve ever wondered why some products are expensive and others are cheap, or how businesses decide on the right price, stick with us. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of what price elasticity is and how it can impact both consumers and businesses. Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of price elasticity.
What is price elasticity?
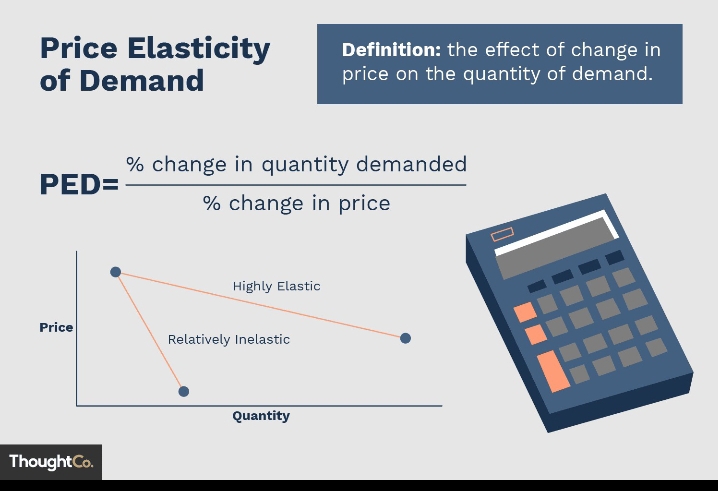
Price elasticity is a way to understand how sensitive customers are to changes in price. It helps us figure out whether people will buy more or less of a product when the price goes up or down.
Imagine you have a favorite snack, like chocolate bars. If the price of chocolate bars suddenly doubled, would you still buy the same amount? Or would you buy less because it’s too expensive now? That’s what price elasticity helps us understand.
On the other hand, if people still buy about the same amount even when the price changes, we say the demand is inelastic. For instance, let’s say the price of salt increases by 50%, but people continue to buy salt in the same quantities. In this case, the demand for salt is inelastic because the price change didn’t have much effect on people’s buying habits.
Understanding price elasticity is important for businesses because it helps them make decisions about pricing. If a product has elastic demand, businesses might need to be careful about raising prices too much, as it could lead to a big drop in sales. On the other hand, if a product has inelastic demand, businesses have more flexibility in adjusting prices without significant changes in demand.
For example, think about gasoline. When the price of gasoline goes up, people still need it to fuel their cars, so they continue to buy it even though it’s more expensive. This shows that the demand for gasoline is inelastic.
By using price elasticity, businesses can set prices that balance their need for profit with what customers are willing to pay. They can also predict how changes in price will affect their sales and adjust their strategies accordingly.
How is price elasticity calculated?
To calculate price elasticity, we use a formula that compares the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price. Let’s break it down step by step:
1. Start by choosing two points on the demand curve: one point before the change in price and another point after the change in price.
2. Calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded: Divide the difference in quantity demanded by the original quantity and multiply by 100. This gives you the percentage change.
3. Calculate the percentage change in price. Divide the difference in price by the original price and multiply by 100. This gives you the percentage change.
Let’s use an example to make it clearer. Suppose the price of a cup of coffee increases from $2 to $2.50, and as a result, the quantity demanded decreases from 100 cups to 80 cups.
Step 1: Choose two points on the demand curve:
- Point A (before the price change) with a price of $2 and quantity demanded of 100 cups, and
- Point B (after the price change) with a price of $2.50 and quantity demanded of 80 cups.
Step 2: Calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded: Percentage change in quantity demanded = ((80 cups – 100 cups) ÷100 cups) × 100 = -20%.
Step 3: Calculate the percentage change in price: Percentage change in price = (($2.50 – $2) ÷ $2) ×100 = 25%.
Step 4: Calculate the price elasticity of demand: Price elasticity of demand = (-20% ÷ 25%) = -0.8.
In this example, the price elasticity of demand is -0.8. The negative sign indicates that the demand is elastic, meaning that a 1% increase in price would result in more than a 0.8% decrease in quantity demanded.
Understanding price elasticity helps businesses determine how responsive customers are to price changes. If the price elasticity is elastic (greater than 1), businesses need to be cautious about raising prices too much, as it could lead to a significant drop in sales. If the price elasticity is inelastic (less than 1), businesses have more flexibility in adjusting prices without a substantial impact on demand.
By calculating price elasticity, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing strategies and better understand how changes in price will affect their sales and revenue.
Why is price elasticity important for businesses?
Price elasticity is really important for businesses because it helps them make smart decisions about pricing their products. Let me explain it in simpler terms.
Imagine you have a store that sells ice cream. Now, let’s say you want to increase the price of your ice cream by 20%. The question is, how will this price increase affect the number of ice cream cones that people buy?
Price elasticity helps us answer that question. If the demand for your ice cream is elastic, it means that when you raise the price by 20%, people will be sensitive to that change and might buy a lot less ice cream. This is because they can easily find alternatives or decide that it’s too expensive. In this case, you need to be careful because raising prices too much could actually lead to a big drop in sales and revenue.
On the other hand, if the demand for your ice cream is inelastic, it means that even if you raise the price by 20%, people will still buy roughly the same amount of ice cream. They might love your ice cream so much that they are willing to pay a bit more for it. In this case, you have more flexibility in adjusting prices without seeing a significant change in demand.
Understanding price elasticity helps businesses set prices that strike a balance between making profits and keeping customers happy. It helps them avoid setting prices too high and losing customers or setting prices too low and not making enough money.
Let’s take another example. Think about luxury handbags. These bags are often expensive, but people who can afford them are often willing to pay the high price because they see the bags as a status symbol. The demand for luxury handbags is usually inelastic because people who want them are not as affected by price changes. Even if the price goes up, they still want to buy the bag.
By knowing the price elasticity of their products, businesses can make better decisions about pricing strategies. They can predict how changes in price will affect their sales and revenue. They can also understand how sensitive their customers are to price changes and adjust prices accordingly. This knowledge helps businesses stay competitive, maintain customer satisfaction, and maximize their profits.




Leave a Review